Background and Epidemiology
- There are two main forms of oesophageal spasm:
- Diffuse oesophageal spasm- where peristaltic contractions are of normal amplitude but are uncoordinated.
- Hypertensive (or nutcracker) oesophagus- where peristaltic contractions are coordinated but excessive in amplitude.
- Both are rare as a primary diagnosis (~1 in 100,000 per year). However, it is thought to be far more common in the general population (e.g. DOS is found in 3-10% of patients who have manometry, particularly in patients >50 years old)
Presentation
- Non-cardiac chest pain is common (particularly in nutcracker oesophagus)
- Retrosternal; onset after meals; often radiates to the back; can be severe
- May mimic cardiac pain e.g. by radiating to the left shoulder
- Dysphagia and Globus (the sensation of a mass in the throat) are also common (moreso in DOS; rarer in nutcracker oesophagus)
- Regurgitation, heartburn/dyspepsia
- Cough and hoarseness can also occur as a result of reflux problems
Investigations
- If cardiac cause is suspected, urgent ECG and troponins are required.
- If there is a convincing history of oesophageal disease,
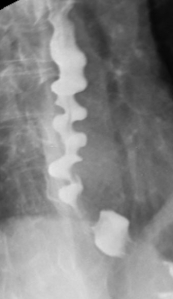
- Barium swallow
- may show a ‘corkscrew oesophagus’ picture
- Barium swallow
- Manometry
- >2 uncoorddinated contractions with 10 consecutive wet swallows or >20% simultaneous contractions is usually what is diagnostic of DOS
- Nutcracker oesophagus is diagnosed by a distal contractile interval of >5000mmHg/s/cm over 10 swallows
- Severe (or jackhammer oesophagus) cases is that >8000mmHg/s/cm
- If neither of these tests are positive, consider endoscopy to rule out strictures/webs, stenosis etc
- If manometry reveals spasm but is not diagnostic for either NO or DOS, USS may help to differentiate.
Management
- It is important to rule out
- Cardiac causes
- GORD- trial with a PPI for one month and see if symptoms improve. Some suggest to do this before investigating with manometry given the epidemiology of motility disorders and GORD, respectively
- If there is confirmed DOS/NO
- As well as a PPI, nifedipine (calcium channel blocker) and nitrates can be used
- Other drugs that can be tried are antidepressants, theophyllines