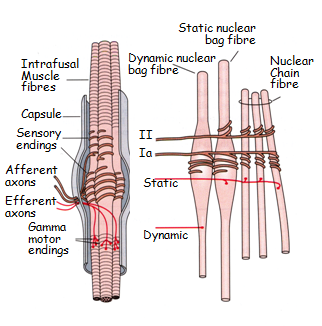
Extrafusal vs Intrafusal muscle fibres
- Extrafusal muscle fibres are the fibres of muscle responsible for muscle contraction and power generation
- innervated by α-motor neurons
- Intrafusal fibres are the fibres of muscle responsible for sensing the muscle length and, more importantly, the rate of change of muscle length.
- the sensory ‘organ’ responsible is themuscle spindle(found in intrafusal fibres)
- signalled via type I(a) fibres (thick, myelinated, fast)- ‘primary spindle endings’- these sense the muscle lengthandrate of change in length AND
- type II fibres (thick, thinly myelinated, not as fast)- ‘secondary spindle endings’- these only really sense muscle length
- these fibres can contract- but the function of which is to avoid over-stretch of the mucle (IMPORTANT- the muscle spindles do NOT contract)
- innervated by small γ-motor neurons (of which there are also two types-
- Static- used in more simple movements
- Dynamic- used in more complex movements
- innervated by small γ-motor neurons (of which there are also two types-
- the sensory ‘organ’ responsible is themuscle spindle(found in intrafusal fibres)
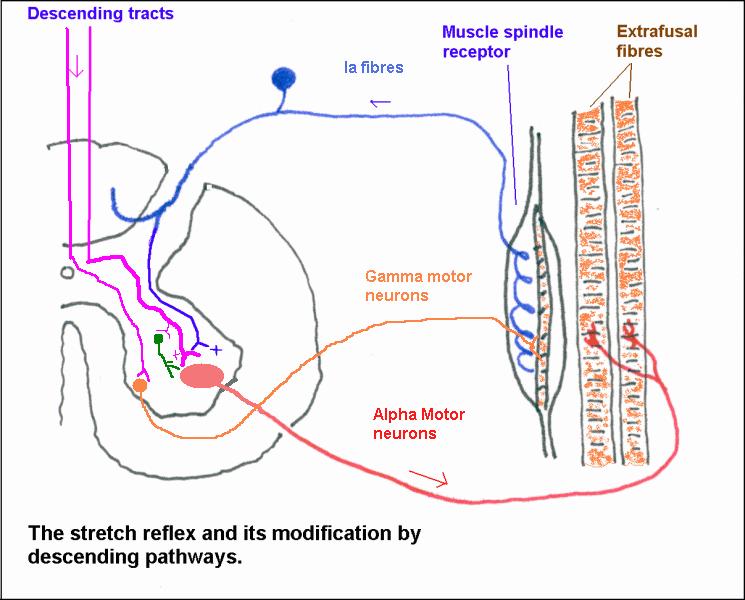
Muscle spindle pathway
The muscle spindle itself
Stretching the intrafusal muscle fibres is termed ‘loading the spindle’. This stretches the sensory endings and increases their of rate discharge. By contrast, when muscle contracts their activity decreases as the spindle becomes ‘unloaded’ .
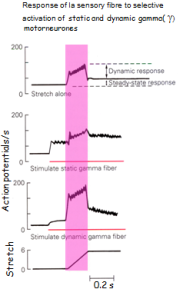
The sensitivity of sensory Ia fibres is increased with recruitment of different gamma motor neurons.
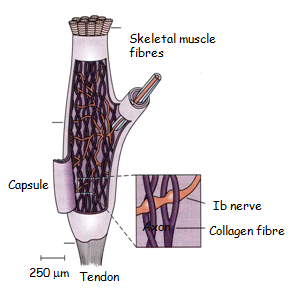
Golgi Tendon Organs
In contrast with muscle spindles that lie within the centre of the muscle belly, Golgi tendon organs are located at muscle tendons. These are complex structures of Golgi sensory neurons (Ib type) wrapped in collagen. When the whole muscle contracts, this is stretched and the sensory neuron is compressed by the collagen, and fires action potentials. These action potentials, unlike those of muscle spindles (a reflex pathway), reaches consciousness and is sensed as ‘physical stretch’.